Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Calcium & bone metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Association between Smoking Status and the Risk of Hip Fracture in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Se-Won Lee, Jun-Young Heu, Ju-Yeong Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):679-689. Published online December 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1760
- 1,216 View
- 66 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Limited longitudinal evidence exists regarding the potential association between smoking status and hip fracture among individuals with type 2 diabetes. We investigated this association using large-scale, nationwide cohort data for the Korean population.
Methods
This nationwide cohort study included 1,414,635 adults aged 40 and older who received Korean National Health Insurance Service health examinations between 2009 and 2012. Subjects with type 2 diabetes were categorized according to their smoking status, amount smoked (pack-years), number of cigarettes smoked per day, and duration of smoking. The results are presented as hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the associations between smoking status parameters and risk of hip fracture in multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analysis.
Results
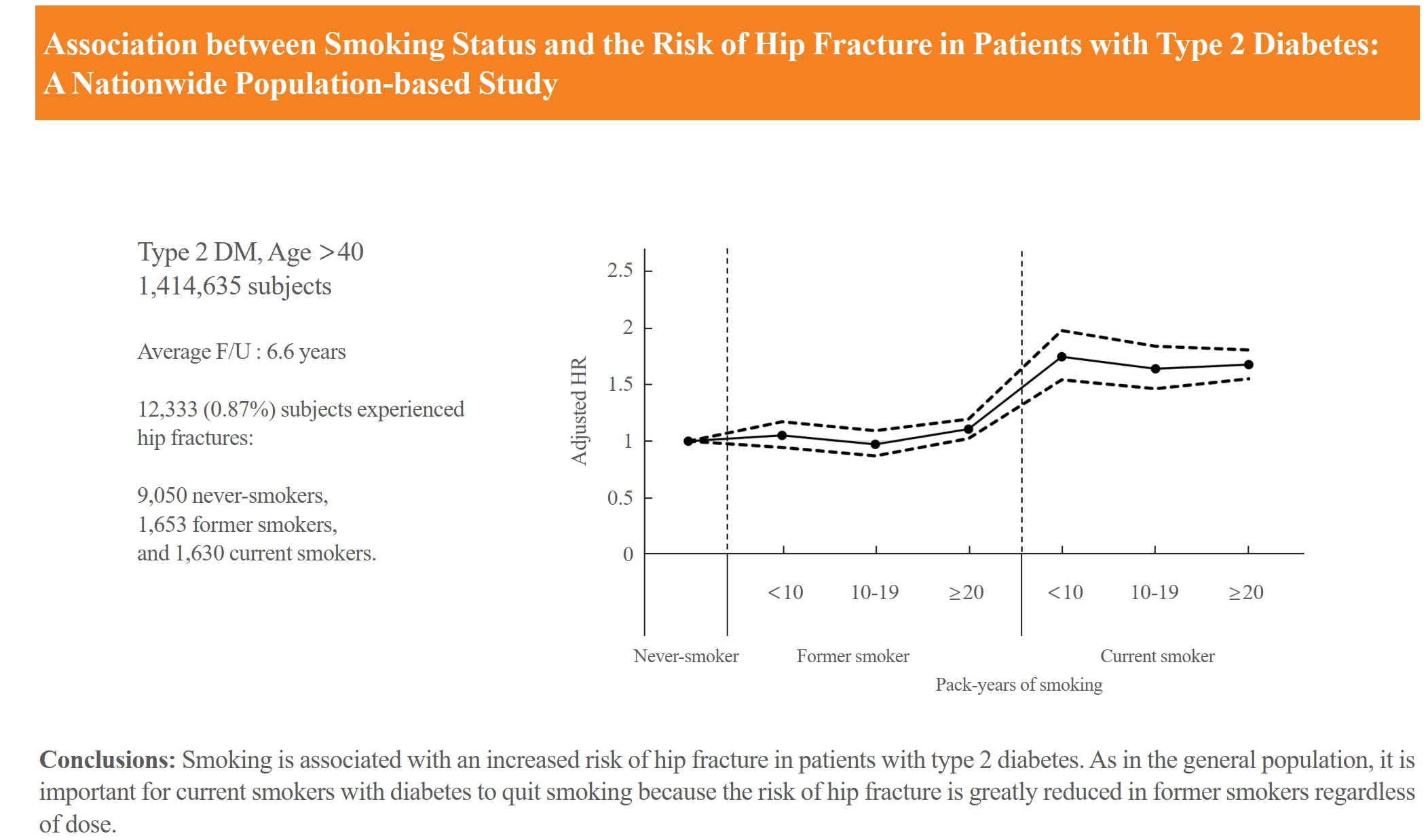
Compared with never-smokers, an increased adjusted HR (aHR) for hip fracture was observed in current smokers (1.681; 95% CI, 1.578 to 1.791), and a comparable aHR for hip fracture was found in former smokers (1.065; 95% CI, 0.999 to 1.136). For former smokers who had smoked 20 pack-years or more, the risk was slightly higher than that for never-smokers (aHR, 1.107; 95% CI, 1.024 to 1.196). The hip fracture risk of female former smokers was similar to that of female current smokers, but the hip fracture risk in male former smokers was similar to that of male never-smokers.
Conclusion
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of hip fracture in patients with type 2 diabetes. Current smokers with diabetes should be encouraged to quit smoking because the risk of hip fracture is greatly reduced in former smokers.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):770-781. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1726

- 1,140 View
- 48 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Elevated γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GTP) levels are associated with metabolic syndrome. We investigated the association of cumulative exposure to high γ-GTP with the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in a large-scale population.
Methods
Using nationally representative data from the Korean National Health Insurance system, 1,640,127 people with 4 years of consecutive γ-GTP measurements from 2009 to 2012 were included and followed up until the end of 2019. For each year of the study period, participants were grouped by the number of exposures to the highest γ-GTP quartile (0–4), and the sum of quartiles (0–12) was defined as cumulative γ-GTP exposure. The hazard ratio for CVD was evaluated using the Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
During the 6.4 years of follow-up, there were 15,980 cases (0.97%) of myocardial infarction (MI), 14,563 (0.89%) of stroke, 29,717 (1.81%) of CVD, and 25,916 (1.58%) of death. Persistent exposure to high γ-GTP levels was associated with higher risks of MI, stroke, CVD, and death than those without such exposure. The risks of MI, stroke, CVD, and mortality increased in a dose-dependent manner according to total cumulative γ-GTP (all P for trend <0.0001). Subjects younger than 65 years, with a body mass index <25 kg/m2, and without hypertension or fatty liver showed a stronger relationship between cumulative γ-GTP and the incidence of MI, CVD, and death.
Conclusion
Cumulative γ-GTP elevation is associated with CVD. γ-GTP could be more widely used as an early marker of CVD risk, especially in individuals without traditional CVD risk factors.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
- Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):426-435. Published online July 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1737

- 2,134 View
- 136 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The effects of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors over the course of long-term treatment remain unclear, and concerns have been raised regarding the role of DPP-4 inhibitors in carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Earlier studies of pancreatic adverse events have reported conflicting results.
Methods
This study analyzed Korean National Health Insurance Service data from January 2009 to December 2012. Patients who had type 2 diabetes mellitus and took two or more oral glucose-lowering drugs (GLDs) were included. Patients prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors (n=51,482) or other GLDs (n=51,482) were matched at a 1:1 ratio using propensity score matching. The risk of pancreatic cancer was calculated using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional-hazards regression analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up period of 7.95 years, 1,051 new cases of pancreatic cancer were identified. The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for DPP-4 inhibitor use was 0.99 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.88 to 1.12) compared with the other GLD group. In an analysis limited to cases diagnosed with pancreatic cancer during hospitalization, the adjusted HR for the use of DPP-4 inhibitors was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.86 to 1.17) compared with patients who took other GLDs. Using the other GLD group as the reference group, no trend was observed for elevated pancreatic cancer risk with increased DPP-4 inhibitor exposure.
Conclusion
In this population-based cohort study, DPP-4 inhibitor use over the course of relatively long-term follow-up showed no significant association with an elevated risk of pancreatic cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes

- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Persistence with Denosumab in Male Osteoporosis Patients: A Real-World, Non-Interventional Multicenter Study
- Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jinyoung Kim, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Tae-Seo Sohn, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):260-268. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1663
- 1,780 View
- 111 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Persistence with denosumab in male patients has not been adequately investigated, although poor denosumab persistence is associated with a significant risk of rebound vertebral fractures.
Methods
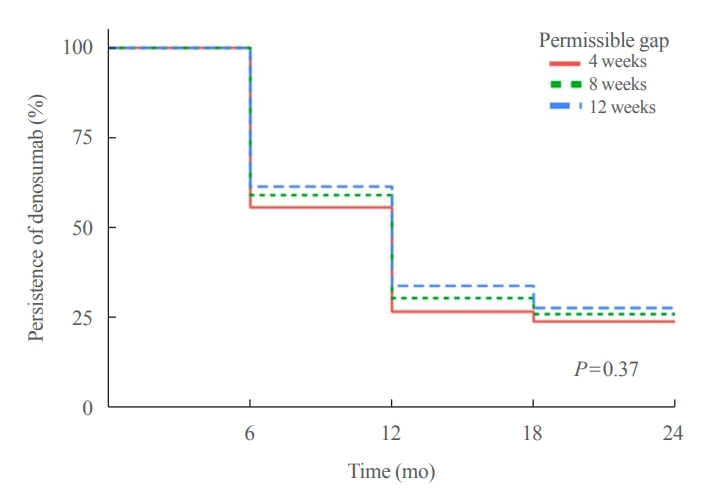
We retrospectively evaluated 294 Korean male osteoporosis patients treated with denosumab at three medical centers and examined their persistence with four doses of denosumab injection over 24 months of treatment. Persistence was defined as the extent to which a patient adhered to denosumab treatment in terms of the prescribed interval and dose, with a permissible gap of 8 weeks. For patients who missed their scheduled treatment appointment(s) during the follow-up period (i.e., no-shows), Cox proportional regression analysis was conducted to explore the factors associated with poor adherence. Several factors were considered, such as age, prior anti-osteoporotic drug use, the treatment provider’s medical specialty, the proximity to the medical center, and financial burdens of treatment.
Results
Out of 294 male patients, 77 (26.2%) completed all four sequential rounds of the denosumab treatment. Out of 217 patients who did not complete the denosumab treatment, 138 (63.6%) missed the scheduled treatment(s). Missing treatment was significantly associated with age (odds ratio [OR], 1.03), prior bisphosphonate use (OR, 0.76), and prescription by non-endocrinologists (OR, 2.24). Denosumab was stopped in 44 (20.3%) patients due to medical errors, in 24 (11.1%) patients due to a T-score improvement over –2.5, and in five (2.3%) patients due to expected dental procedures.
Conclusion
Our study showed that only one-fourth of Korean male osteoporosis patients were fully adherent to 24 months of denosumab treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Denosumab
Reactions Weekly.2023; 1963(1): 206. CrossRef
- Denosumab

- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Repeated Low High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Population- Based Study in Korea
- Jinyoung Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):303-311. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1332

- 4,702 View
- 155 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) plays an important role in the reverse cholesterol transport pathway and prevents atherosclerosis-mediated disease. It has also been suggested that HDL-C may be a protective factor against cancer. However, an inverse correlation between HDL-C and cancer has not been established, and few studies have explored thyroid cancer.
Methods
The study participants received health checkups provided by the Korean National Health Insurance Service from 2009 to 2013 and were followed until 2019. Considering the variability of serum HDL-C level, low HDL-C level was analyzed by grouping based on four consecutive health checkups. The data analysis was performed using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models.
Results
A total of 3,134,278 total study participants, thyroid cancer occurred in 16,129. In the crude model, the hazard ratios for the association between repeatedly measured low HDL-C levels and thyroid cancer were 1.243, 1.404, 1.486, and 1.680 (P for trend <0.01), respectively, which were significant even after adjusting for age, sex, lifestyle factors, and metabolic diseases. The subgroup analysis revealed that low HDL-C levels likely had a greater impact on the group of patients with central obesity (P for interaction= 0.062), high blood pressure (P for interaction=0.057), impaired fasting glucose (P for interaction=0.051), and hyperlipidemia (P for interaction=0.126).
Conclusion
Repeatedly measured low HDL-C levels can be considered a risk factor for cancer as well as vascular disease. Low HDL-C levels were associated with the risk of thyroid cancer, and this correlation was stronger in a metabolically unhealthy population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between organophosphate flame retardant exposure and lipid metabolism: data from the 2013–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Fu-Jen Cheng, Kai-Fan Tsai, Kuo-Chen Huang, Chia-Te Kung, Wan-Ting Huang, Huey-Ling You, Shau-Hsuan Li, Chin-Chou Wang, Wen-Chin Lee, Hsiu-Yung Pan
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low serum total cholesterol levels predict inferior prognosis of patients with POEMS syndrome
Jue Zhang, Ting Zhang, Ye Yao, Xuxing Shen, Yuanyuan Jin, Run Zhang, Lijuan Chen
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipoprotein alterations in endocrine disorders - a review of the recent developments in the field
Michal Olejarz, Ewelina Szczepanek-Parulska, Marek Ruchala
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Carbohydrate, Lipid, and Apolipoprotein Biomarkers in Blood and Risk of Thyroid Cancer: Findings from the AMORIS Cohort
Xue Xiao, Yi Huang, Fetemeh Sadeghi, Maria Feychting, Niklas Hammar, Fang Fang, Zhe Zhang, Qianwei Liu
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 520. CrossRef - Altered serum lipid levels are associated with prognosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma and influenced by utility of rituximab
Fei Wang, Luo Lu, HuiJuan Chen, Yanhua Yue, Yanting Sun, Feng Yan, Bai He, Rongrong Lin, Weiying Gu
Annals of Hematology.2023; 102(2): 393. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and carcinogenesis
Meijuan Tan, Shijie Yang, Xiequn Xu
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 34(5): 303. CrossRef - Low Serum Cholesterol Level Is a Significant Prognostic Factor That Improves CLL-IPI in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
Rui Gao, Kaixin Du, Jinhua Liang, Yi Xia, Jiazhu Wu, Yue Li, Bihui Pan, Li Wang, Jianyong Li, Wei Xu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(8): 7396. CrossRef - Do metabolic factors increase the risk of thyroid cancer? a Mendelian randomization study
Weiwei Liang, FangFang Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of causal association between differentiated thyroid cancer and disordered serum lipid profile: a Mendelian randomization study
Qiang Ma, Yu Li, Lijuan An, Liang Guo, Xiaokang Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors and diagnostic prediction models for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xiaowen Zhang, Yuyang Ze, Jianfeng Sang, Xianbiao Shi, Yan Bi, Shanmei Shen, Xinlin Zhang, Dalong Zhu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exposure to multiple trace elements and thyroid cancer risk in Chinese adults: A case-control study
Jia-liu He, Hua-bing Wu, Wen-lei Hu, Jian-jun Liu, Qian Zhang, Wei Xiao, Ming-jun Hu, Ming Wu, Fen Huang
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2022; 246: 114049. CrossRef
- Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Frequency of Exposure to Impaired Fasting Glucose and Risk of Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Mee Kyoung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1007-1015. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1218
- 3,852 View
- 126 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Metabolic abnormalities, such as impaired fasting glucose (IFG), are dynamic phenomena; however, it is unclear whether the timing of IFG exposure and cumulative exposure to IFG are related to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality risk.
Methods
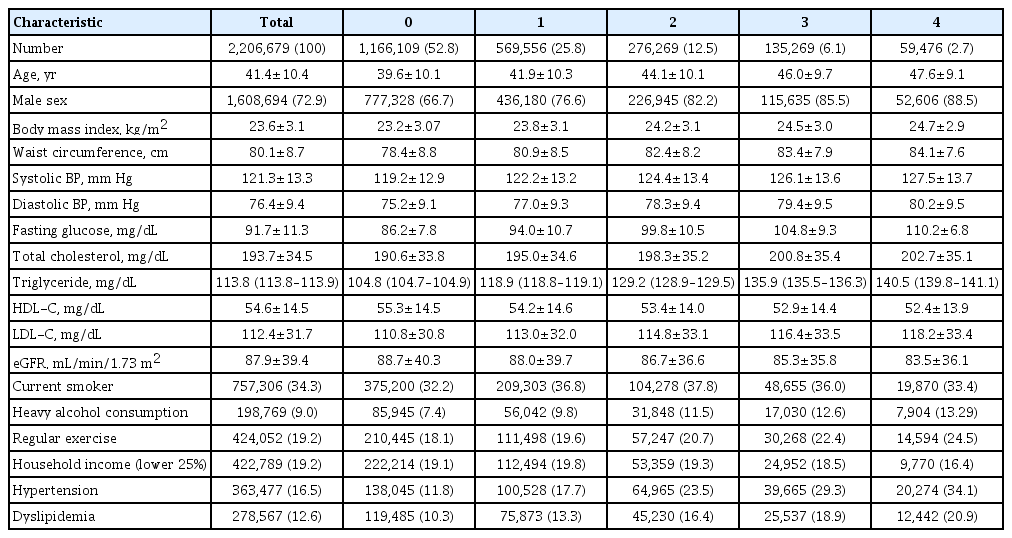
Data were extracted from a nationwide population-based cohort in South Korea for adults (n=2,206,679) who were free of diabetes and had 4 years of consecutive health examination data. Fasting blood glucose levels of 100 to 125 mg/dL were defined as IFG, and the number of IFG diagnoses for each adult in the 4-year period was tabulated as the IFG exposure score (range, 0 to 4). Adults with persistent IFG for the 4-year period received a score of 4.
Results
The median follow-up was 8.2 years. There were 24,820 deaths, 13,502 cases of stroke, and 13,057 cases of myocardial infarction (MI). IFG exposure scores of 1, 2, 3, and 4 were associated with all-cause mortality (multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08 to 1.15; aHR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.20; aHR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.15 to 1.25; aHR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.11 to 1.25, respectively) compared with an IFG exposure score of 0. Adjusting for hypertension and dyslipidemia attenuated the slightly increased risk of MI or stroke associated with high IFG exposure scores, but significant associations for allcause mortality remained.
Conclusion
The intensity of IFG exposure was associated with an elevated risk of all-cause mortality, independent of cardiovascular risk factors. The association between IFG exposure and CVD risk was largely mediated by the coexistence of dyslipidemia and hypertension. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease
Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
npj Parkinson's Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and Validation of a Model for Predicting Impaired Fasting Glucose Based on More Than 4000 General Population
Cuicui Wang, Xu Zhang, Chenwei Li, Na Li, Xueni Jia, Hui Zhao
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 1415. CrossRef - Factors Affecting High Body Weight Variability
Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 163. CrossRef - Exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of stroke in adults: a meta-analysis
Min Cheol Chang, Seung Min Chung, Sang Gyu Kwak
Reviews on Environmental Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Longitudinal Retrospective Observational Study on Obesity Indicators and the Risk of Impaired Fasting Glucose in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women
Myung Ji Nam, Hyunjin Kim, Yeon Joo Choi, Kyung-Hwan Cho, Seon Mee Kim, Yong-Kyun Roh, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Yong-Gyu Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Do-Hoon Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(10): 2795. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Lipid cutoffs for increased cardiovascular disease risk in non-diabetic young people
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 29(14): 1866. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease

- Bone Metabolism
- Comparison of the Effects of Various Antidiabetic Medication on Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jeonghoon Ha, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Seung Hyun Ko, Moo Il Kang, Sung Dae Moon, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):895-903. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1026
- 6,151 View
- 230 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Prospective comparative studies on the effects of various antidiabetic agents on bone metabolism are limited. This study aimed to assess changes in bone mass and biochemical bone markers in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This prospective, multicenter, open-label, comparative trial included 264 patients with T2DM. Patients who had received a metformin, or sulfonylurea/metformin combination (Group 1); a thiazolidinedione combination (Group 2); a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (gemigliptin) combination (Group 3); or an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (empagliflozin) combination (Group 4) were prospectively treated for 12 months; bone mineral density (BMD) and bone turnover marker (BTM) changes were evaluated.
Results
The femoral neck BMD percentage changes were −0.79%±2.86% (Group 1), −2.50%±3.08% (Group 2), −1.05%±2.74% (Group 3), and −1.24%±2.91% (Group 4) (P<0.05). The total hip BMD percentage changes were −0.57%±1.79% (Group 1), −1.74%±1.48% (Group 2), −0.75%±1.87% (Group 3), and −1.27%±1.72% (Group 4) (P<0.05). Mean serum BTM (C-terminal type 1 collagen telopeptide and procollagen type 1 amino-terminal propeptide) levels measured during the study period did not change over time or differ between groups.
Conclusion
Significant bone loss in the femoral neck and total hip was associated with thiazolidinedione combination regimens. However, bone loss was not significantly associated with combination regimens including gemigliptin or empagliflozin. Caution should be exercised during treatment with antidiabetic medications that adversely affect the bone in patients with diabetes at a high risk of bone loss. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Meta-Analysis on the Association Between DPP-4 Inhibitors and Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis
Lili Huang, Wei Zhong, Xinghuan Liang, Huijuan Wang, Shi-en Fu, Zuojie Luo
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2024; 27(1): 101455. CrossRef - A multicentre, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized, parallel comparison, phase 3 trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pioglitazone add‐on therapy in type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin and dapagliflozin
Soo Lim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Kyung‐Wan Min, Chang Beom Lee, Sang Yong Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Nan Hee Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Jong Chul Won, Hyuk Sang Kwon, Mi Kyung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, In‐Kyung Jeong, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Bone Turnover Markers with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Microvascular Complications: A Matched Case-Control Study
Yilin Hou, Xiaoyu Hou, Qian Nie, Qiuyang Xia, Rui Hu, Xiaoyue Yang, Guangyao Song, Luping Ren
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1177. CrossRef - Complementary effects of dapagliflozin and lobeglitazone on metabolism in a diet-induced obese mouse model
Yun Kyung Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Ji In Lee, Bo Yoon Choi, Hyen Chung Cho, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 957: 175946. CrossRef
- Meta-Analysis on the Association Between DPP-4 Inhibitors and Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis

- Clinical Study
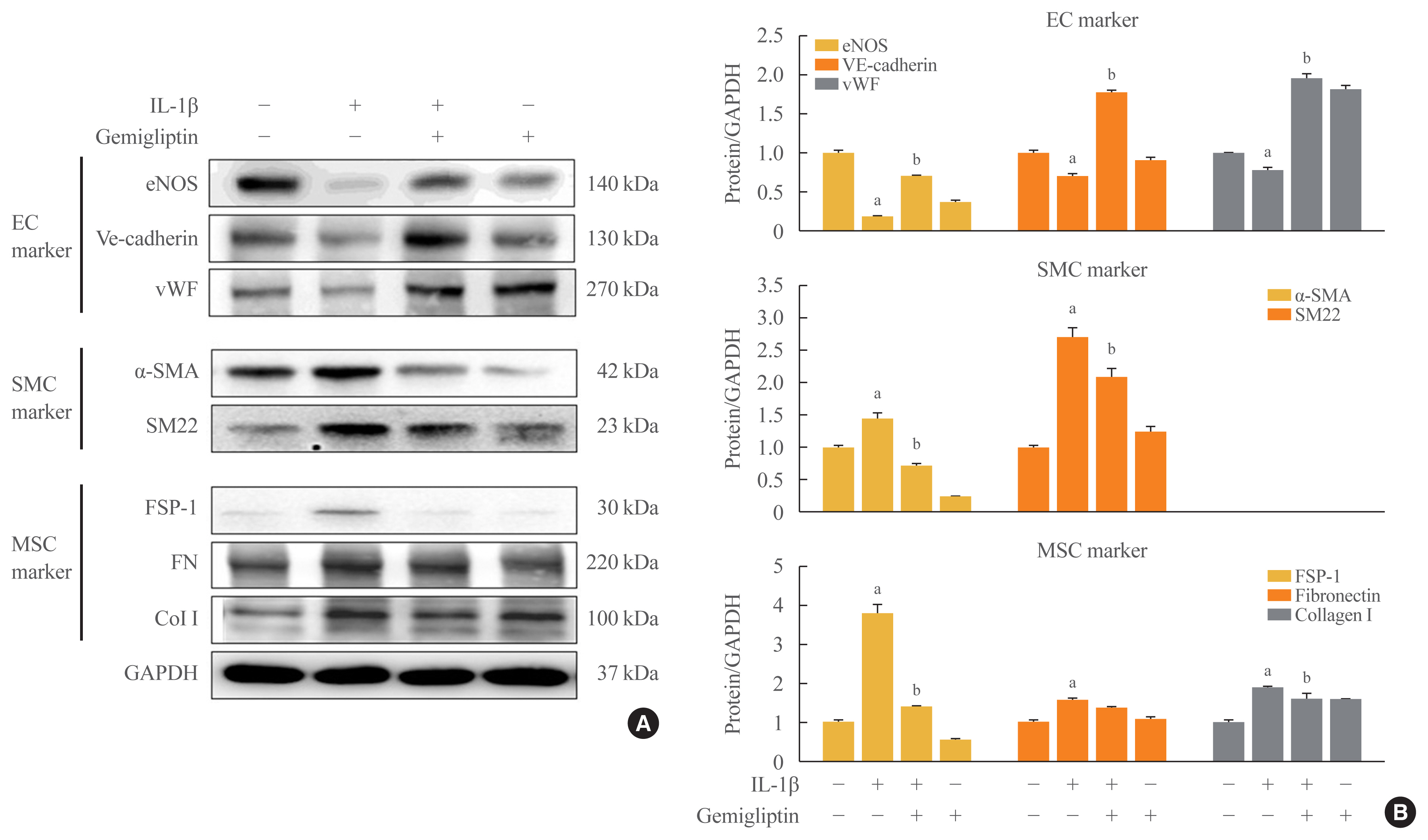
- Gemigliptin Inhibits Interleukin-1β–Induced Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition via Canonical-Bone Morphogenetic Protein Pathway
- Oak-Kee Hong, Seong-Su Lee, Soon Jib Yoo, Min-Kyung Lee, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):384-395. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.384
- 6,777 View
- 139 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) contributes to inflammatory conditions inducing conversion of endothelial cells (ECs) into activated fibroblasts, promoting fibrotic diseases. Pro-inflammatory cytokine is the most potent inducer of EndMT. We investigated inhibition of interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced EndMT by gemigliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor.
Methods
We exposed human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to 10 ng/mL IL-1β/20 μM gemigliptin and analyzed the expression of endothelial, smooth muscle, mesenchymal, and osteoblastic markers, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), Smad, and non-Smad signaling pathway proteins.
Results
Morphological changes showed gemigliptin blocked IL-1β-induced EndMT, upregulated EC markers, and downregulated smooth muscle and mesenchymal markers. IL-1β activation of HUVECs is initiated by the BMP/Smad and non-smad BMP signaling pathways. Gemigliptin inhibited IL-1β induction of BMP2 and 7, activin receptor type IA, BMP receptor type IA, and BMP receptor type II. Reversal of IL-1β-mediated inhibition of BMP-induced Smad1/5/8, Smad2, and Smad3 phosphorylation by gemigliptin suggests involvement of the Smad pathway in gemigliptin action. In the non-Smad BMP pathway, gemigliptin treatment significantly increased the deactivation of extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK), p38, and JNK by IL-1β. Gemigliptin treatment suppressed BMP-2-induced expression of key osteoblastic markers including osterix, runt-related transcription factor 2, and hepcidin during IL-1β-induced EndMT.
Conclusion
We demonstrated a novel protective mechanism of gemigliptin against fibrosis by suppressing IL-1β-induced EndMT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Injured Endothelial Cell: A Risk Factor for Pulmonary Fibrosis
Weiming Zhao, Lan Wang, Yaxuan Wang, Hongmei Yuan, Mengxia Zhao, Hui Lian, Shuaichen Ma, Kai Xu, Zhongzheng Li, Guoying Yu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(10): 8749. CrossRef - Tissue fibrosis induced by radiotherapy: current understanding of the molecular mechanisms, diagnosis and therapeutic advances
Zuxiang Yu, Chaoyu Xu, Bin Song, Shihao Zhang, Chong Chen, Changlong Li, Shuyu Zhang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - MiRNAs in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Markers and Effectors
Mor Zaaroor Levy, Noa Rabinowicz, Maia Yamila Kohon, Avshalom Shalom, Ariel Berl, Tzipi Hornik-Lurie, Liat Drucker, Shelly Tartakover Matalon, Yair Levy
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 629. CrossRef - Recent advance in treatment of atherosclerosis: Key targets and plaque-positioned delivery strategies
Li Li, Sainan Liu, Jianying Tan, Lai Wei, Dimeng Wu, Shuai Gao, Yajun Weng, Junying Chen
Journal of Tissue Engineering.2022; 13: 204173142210885. CrossRef - Vascular Calcification: New Insights Into BMP Type I Receptor A
Zhixing Niu, Guanyue Su, Tiantian Li, Hongchi Yu, Yang Shen, Demao Zhang, Xiaoheng Liu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Yi-Shen-Hua-Shi Granule Alleviates Adriamycin-Induced Glomerular Fibrosis by Suppressing the BMP2/Smad Signaling Pathway
Zhuojing Tan, Yachen Si, Yan Yu, Jiarong Ding, Linxi Huang, Ying Xu, Hongxia Zhang, Yihan Lu, Chao Wang, Bing Yu, Li Yuan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Panax notoginseng Suppresses Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Expression in EA.hy926 Endothelial Cells by Inhibiting the Noncanonical NF-κB and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways
Tsu-Ni Ping, Shu-Ling Hsieh, Jyh-Jye Wang, Jin-Bor Chen, Chih-Chung Wu
Plants.2022; 11(23): 3265. CrossRef - Vascular calcification: New insights into endothelial cells
Cheng Yuan, Lihua Ni, Changjiang Zhang, Xiaorong Hu, Xiaoyan Wu
Microvascular Research.2021; 134: 104105. CrossRef - Concentrated small extracellular vesicles from menstrual blood-derived stromal cells improve intrauterine adhesion, a pre-clinical study in a rat model
Siwen Zhang, Qiyuan Chang, Pingping Li, Xiaoyu Tong, Yi Feng, Xinyao Hao, Xudong Zhang, Zhengwei Yuan, Jichun Tan
Nanoscale.2021; 13(15): 7334. CrossRef
- Injured Endothelial Cell: A Risk Factor for Pulmonary Fibrosis

- Clinical Study
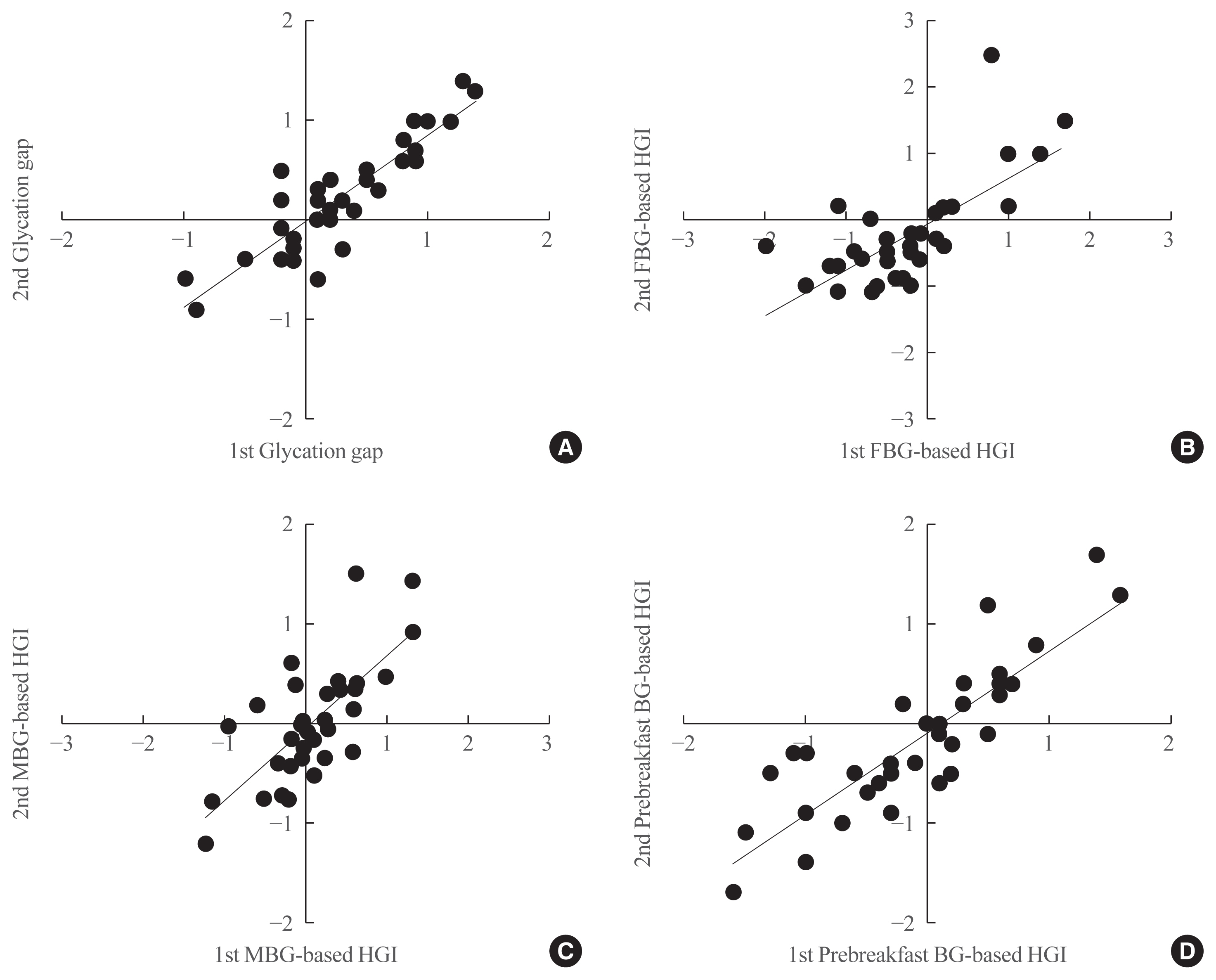
- Consistency of the Glycation Gap with the Hemoglobin Glycation Index Derived from a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
- Han Na Joung, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Mee Kyoung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):377-383. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.377
- 5,859 View
- 113 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Discordances between glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and glycemic control are common in clinical practice. We aimed to investigate the consistency of the glycation gap with the hemoglobin glycation index (HGI).
Methods
From 2016 to 2019, 36 patients with type 2 diabetes were enrolled. HbA1c, glycated albumin (GA), and fasting blood glucose levels were simultaneously measured and 72-hour continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) was performed on the same day. Repeated tests were performed at baseline and 1 month later, without changing patients’ diabetes management. The HGI was calculated as the difference between the measured HbA1c and the predicted HbA1c that was derived from CGM. The glycation gap was calculated as the difference between the measured and GA-based predicted HbA1c levels.
Results
Strong correlations were found between the mean blood glucose (MBG)-based HGI and the prebreakfast glucose-based HGI (r=0.867, P<0.001) and between the glycation gap and the MBG-based HGI (r=0.810, P<0.001). A close correlation was found between the MBG-based HGI at baseline and that after 1 month (r=0.729, P<0.001), with a y-intercept of 0 and a positive slope.
Conclusion
The HGI and glycation gap were highly reproducible, and the magnitudes of repeated determinations were closely correlated. Patients with similar mean glucose levels may have significantly different HbA1c levels. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with hemoglobin glycation index in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus: The FGM‐Japan study
Naoki Sakane, Yushi Hirota, Akane Yamamoto, Junnosuke Miura, Hiroko Takaike, Sari Hoshina, Masao Toyoda, Nobumichi Saito, Kiminori Hosoda, Masaki Matsubara, Atsuhito Tone, Satoshi Kawashima, Hideaki Sawaki, Tomokazu Matsuda, Masayuki Domichi, Akiko Suganu
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(4): 582. CrossRef - The Fast-Glycator Phenotype, Skin Advanced Glycation End Products, and Complication Burden Among People With Type 1 Diabetes
Alberto Maran, Mario Luca Morieri, Daniele Falaguasta, Angelo Avogaro, Gian Paolo Fadini
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(10): 2439. CrossRef - Hemoglobin glycation index, calculated from a single fasting glucose value, as a prediction tool for severe hypoglycemia and major adverse cardiovascular events in DEVOTE
Klara R Klein, Edward Franek, Steven Marso, Thomas R Pieber, Richard E Pratley, Amoolya Gowda, Kajsa Kvist, John B Buse
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(2): e002339. CrossRef
- Factors associated with hemoglobin glycation index in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus: The FGM‐Japan study

- Clinical Study
- Short-Term Effects of Beraprost Sodium on the Markers for Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Microalbuminuria
- Yun Mi Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyung Mook Choi, Won-Young Lee, Eun-Gyoung Hong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):398-405. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.398
- 5,335 View
- 60 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background To evaluate the changes in cardiovascular risk markers including pulse wave velocity (PWV), microalbuminuria, inflammatory cytokines, and adhesion molecules after treatment with beraprost sodium (BPS) in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Methods This was a multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with microalbuminuria were included. The primary endpoints were changes in microalbuminuria in spot urine and PWV after BPS or placebo (PCB) treatment for 24 weeks. The secondary endpoints were changes in clinical and metabolic parameters.
Results A total of 52 patients completed the 24-week trial. Changes in PWV were not different significantly in the BPS and PCB groups (right,
P =0.16; left,P =0.11). Changes in microalbuminuria were 14.2±157.0 and 34.5±146.6 (µg/mg Cr) in the BPS and PCB groups, respectively (P =0.63). Subgroup analysis in the high blood pressure (BP) group (baseline systolic BP >120 mm Hg and diastolic BP >80 mm Hg), showed that microalbuminuria decreased by −47.6 in the BPS group compared with an increase by 116.4 (µg/mg Cr) in the PCB group (P =0.04). Also, in the large waist circumference group (>95 cm), microalbuminuria decreased significantly in the BPS group (P =0.04).Conclusion Short-term treatment of BPS for patients with diabetic nephropathy did not show significant improvement in various cardiovascular risk factors. However, BPS significantly decreased microalbuminuria in study subjects with higher cardiovascular risk such as high BP or large waist circumference.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical efficacy of beraprost sodium in treating chronic kidney disease: A six-month prospective study
Chen Sun, Xin Wu, Xin Zhang, Shulin Li, Ruoyu Jia, Dong Sun
Heliyon.2024; 10(2): e24156. CrossRef - Clinical efficacy and safety of beraprost sodium in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome: A meta-analysis
Peng Yan, Ben Ke, Xiangdong Fang
Medicine.2023; 102(42): e34958. CrossRef - Dysregulated coagulation system links to inflammation in diabetic kidney disease
Mengyun Xiao, Donge Tang, Shaodong Luan, Bo Hu, Wenyu Gong, Wolfgang Pommer, Yong Dai, Lianghong Yin
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of beraprost sodium on renal function and cardiometabolic profile in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Peyman Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, Reza Tabrizi, Kamran Hessami, Mojtaba Shabani-Borujeni, Mahnaz Hosseini-Bensenjan, Shahla Rezaei, Mohammad Jalali, Pedram Keshavarz, Fariba Ahmadizar
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 54(1): 111. CrossRef - Thrombocytopenia in COVID‑19 and vaccine‑induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Styliani Geronikolou, Işil Takan, Athanasia Pavlopoulou, Marina Mantzourani, George Chrousos
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Platelets in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Ukhti Jamil Rustiasari, Joris J. Roelofs
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8270. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef
- Clinical efficacy of beraprost sodium in treating chronic kidney disease: A six-month prospective study

- Clinical Study
- Comparison of Natural Course between Thyroid Cancer Nodules and Thyroid Benign Nodules
- Kyun-Jin Yun, Jeonghoon Ha, Min-Hee Kim, Ye Young Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):195-202. Published online June 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.195
- 4,526 View
- 65 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The natural course of thyroid cancer nodules and benign nodules is different. This study was to compare the changes in size between thyroid cancer nodules and thyroid benign nodules. The risk factors associated with the changes of thyroid cancer nodules were assessed.
Methods This study contains retrospective observational and prospective analysis. A total of 113 patients with 120 nodules were recruited in the cancer group, and 116 patients with 119 nodules were enrolled in the benign group. Thyroid ultrasonography was performed at least two times at more than 1-year interval.
Results The mean follow-up durations were 29.5±18.8 months (cancer group) and 31.9±15.8 months (benign group) (
P =0.32). The maximum diameter change in length was 0.36±0.97 mm/year in the cancer group and –0.04±0.77 mm/year in the benign group (P <0.01). The volume was significantly increased in the cancer group compared with the benign group (0.06±0.18 mL/year vs. 0.004±0.05 mL/year, respectively,P <0.01; 26.9%±57.9%/year vs. 1.7%±26.0%/year,P <0.01). Initial maximum diameter (β=0.02,P <0.01) and initial volume (β=0.13,P <0.01) were significantly associated with volume change (mL)/year. Initial maximum standardized uptake value did not predict the nodule growth.Conclusion It is suggested that thyroid cancer nodules progress rapidly compared with benign nodules. Initial size and volume of nodule were independent risk factors for cancer nodule growth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- RAS-Mutated Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: Prevalence of Malignancy and Behavior Under Active Surveillance
Hannah J. Sfreddo, Elizabeth S. Koh, Karena Zhao, Christina E. Swartzwelder, Brian R. Untch, Jennifer L. Marti, Benjamin R. Roman, Jared Dublin, Ronald S. Wang, Rong Xia, Jean-Marc Cohen, Bin Xu, Ronald Ghossein, Babak Givi, Jay O. Boyle, R. Michael Tuttl
Thyroid®.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound for the assessment of thyroid nodules: an overview for non-radiologists
Conor Hamill, Peter Ellis, Philip C Johnston
British Journal of Hospital Medicine.2022; 83(7): 1. CrossRef - Цитологічно підтверджений вузловий зоб у членів Українсько-Американського когортного дослідження: дескриптивний аналіз результатів обстеження за 1998- 2015 роки
M.D. Tronko, L.S. Strafun, H.M. Terekhova, H.A. Zamotayeva, I.P. Pasteur
Endokrynologia.2022; 27(1): 5. CrossRef - A Computational Study on the Role of Parameters for Identification of Thyroid Nodules by Infrared Images (and Comparison with Real Data)
José R. González, Charbel Damião, Maira Moran, Cristina A. Pantaleão, Rubens A. Cruz, Giovanna A. Balarini, Aura Conci
Sensors.2021; 21(13): 4459. CrossRef - Ultrasound in active surveillance for low-risk papillary thyroid cancer: imaging considerations in case selection and disease surveillance
Sangeet Ghai, Ciara O’Brien, David P. Goldstein, Anna M. Sawka, Lorne Rotstein, Dale Brown, John de Almeida, Patrick Gullane, Ralph Gilbert, Douglas Chepeha, Jonathan Irish, Jesse Pasternak, Shereen Ezzat, James P. Brierley, Richard W. Tsang, Eric Monteir
Insights into Imaging.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between various thyroid gland diseases, TSH values and thyroid cancer: a case–control study
Leif Schiffmann, Karel Kostev, Matthias Kalder
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology.2020; 146(11): 2989. CrossRef - Combination of peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma and retinoid X receptor agonists induces sodium/iodide symporter expression and inhibits cell growth of human thyroid cancer cells
Jui-Yu Chen, Jane-Jen Wang, Hsin-Chen Lee, Chin-Wen Chi, Chen-Hsen Lee, Yi-Chiung Hsu
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2020; 83(10): 923. CrossRef - Growth rates of malignant and benign thyroid nodules in an ultrasound follow-up study: a retrospective cohort study
Michael Cordes, Theresa Ida Götz, Karen Horstrup, Torsten Kuwert, Christian Schmidkonz
BMC Cancer.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- RAS-Mutated Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: Prevalence of Malignancy and Behavior Under Active Surveillance

- Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Dyslipidemia in Koreans
- Jee-Sun Jeong, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):30-35. Published online March 20, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.30
- 4,996 View
- 46 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The prevalence of hypercholesterolemia in Koreans 30 years old and over was 19.5% in 2015 according to the Korean Nutrition and Health Examination Survey, which means that one-fifth of adults had hypercholesterolemia. The prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia in adults 30 years of age and older was 16.8% in 2015, and men had a 2-fold higher prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia than women (23.9% vs. 10.4%). The awareness of hypercholesterolemia in Koreans was higher in women than among men (62.4% vs. 51.4%). It increased with age; the level of awareness in participants 30 to 49 years of age (32.1% in men and 32.6% in women) was less than half of that observed among respondents ≥65 years old (77.5% in men and 78.0% in women). Regular check-ups for dyslipidemia and the active management thereof are urgent in Korean men aged 30 to 49. In women, the perimenopausal period is crucial for the prevention and management of metabolic syndrome, including dyslipidemia. Overall, improvements in awareness and treatment in the age group of 30 to 49 years in both men and women remain necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between weekend catch-up sleep and dyslipidemia among Korean workers
Ye Seul Jang, Yu Shin Park, Kyungduk Hurh, Eun-Cheol Park, Sung-In Jang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between meat intake and the risk of coronary heart disease in Korean men using the Framingham risk score: A prospective cohort study
Jiwon Jeong, Kyungjoon Lim, Sangah Shin
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(6): 1158. CrossRef - New-onset dyslipidemia in adult cancer survivors from medically underserved areas: a 10-year retrospective cohort study
Yun Hwa Jung, IL Yun, Eun-Cheol Park, Sung-In Jang
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Paradigm Shift in Dyslipidemia Management in Primary Care: A 12-Month Cohort Study
Jun Hwa Hong, Ung Jeon, Won-Yong Shin, Weon Kim, Kayeon Seong, Sang-Ho Park, Hee-dong Kim, Joong-Wha Chung, Jaehyuk Choi
Clinical Therapeutics.2022; 44(5): 698. CrossRef - Temporal trends in heart failure over 11 years in the aging Korean population: A retrospective study using the national health insurance database
Dong-Hyuk Cho, Chan Joo Lee, Jung-Woo Son, Jimi Choi, Jinseub Hwang, Byung-Su Yoo, Yajing Wang
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0279541. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk and undertreatment of dyslipidemia in lung cancer survivors: A nationwide population-based study
In Young Cho, Kyungdo Han, Dong Wook Shin, Sang Hyun Park, Dong Woog Yoon, Sujeong Shin, Su-Min Jeong, Jong Ho Cho
Current Problems in Cancer.2021; 45(1): 100615. CrossRef - Association Between Blood Heavy Metal Concentrations and Dyslipidemia in the Elderly
Xingmeng Zhu, Yong Fan, Jie Sheng, Ling Gu, Qi Tao, Rui Huang, Kaiyong Liu, Linsheng Yang, Guimei Chen, Hongjuan Cao, Kaichun Li, Fangbiao Tao, Sufang Wang
Biological Trace Element Research.2021; 199(4): 1280. CrossRef - The prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and associated risk factors in Al-Kharj population, Saudi Arabia: a cross-sectional survey
Jamaan Al-Zahrani, Mamdouh M. Shubair, Sameer Al-Ghamdi, Abdullah A. Alrasheed, Abdulrahman A. Alduraywish, Fayez Saud Alreshidi, Saeed Mastour Alshahrani, Majid Alsalamah, Badr F. Al-Khateeb, Aljawharah Ibraheem Ashathri, Ashraf El-Metwally, Khaled K. Al
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of dyslipidemia among diabetes mellitus patients and predictors of optimal dyslipidemia control: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Seung Jae Kim, Oh. Deog Kwon, Kyung-Soo Kim
Lipids in Health and Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Case Report of a Patient Diagnosed with Fatty Liver Accompanied by Hypertriglyceridemia
Soyoung Hur, Soyeon An, Eujin Kim, Cho-Hyun Hwang, Eungyeong Jang, Youngchul Kim, Jang-Hoon Lee
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2021; 42(2): 207. CrossRef - Changes in Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Residents of the Siberian Region (According to Epidemiological Studies)
G. V. Artamonova, S. A. Maksimov, D. P. Tsygankova, E. D. Bazdyrev, E. V. Indukaeva, T. A. Mulerova, E. B. Shapovalova, A. S. Agienko, O. V. Nakhratova, O. L. Barbarash
Rational Pharmacotherapy in Cardiology.2021; 17(3): 362. CrossRef - Pre-existing Depression among Newly Diagnosed Dyslipidemia Patients and Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Jihoon Andrew Kim, Seulggie Choi, Daein Choi, Sang Min Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 307. CrossRef - Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal attainment rates in high-risk patients with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
Ye Seul Yang, Bo Ram Yang, Mi-Sook Kim, Yunji Hwang, Sung Hee Choi
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for cardiovascular disease in ethnic Europeans and Koreans living in the Primorsky Krai
D. Yu. Bogdanov, V. A. Nevzorova, V. B. Shumatov, E. A. Kondrashova, E. Yu. Shestopalov
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2020; 19(1): 40. CrossRef - Effect of Smartphone-Based Lifestyle Coaching App on Community-Dwelling Population With Moderate Metabolic Abnormalities: Randomized Controlled Trial
So Mi Jemma Cho, Jung Hyun Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyungseon Yeom, Su Jin Lee, Yong Woo Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(10): e17435. CrossRef - Risk factors for cardiovascular disease in ethnic Europeans and Koreans living in the Primorsky Krai
D. Yu. Bogdanov, V. A. Nevzorova, V. B. Shumatov, E. A. Kondrashova, E. Yu. Shestopalov
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2020; 19(1): 40. CrossRef - The effect of healthy Nordic diet on cardio-metabolic markers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
Nahid Ramezani-Jolfaie, Mohammad Mohammadi, Amin Salehi-Abargouei
European Journal of Nutrition.2019; 58(6): 2159. CrossRef - Association between Low-Intensity Smoking and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Men
Minji Park, Seran Min, Yu Jin Cho, Sunwoo Kim, Hyuktae Kwon, Hee-Kyung Joh, Bumjo Oh, Seung-Won Oh, Ho Chun Choi, Cheol Min Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco.2019; 10(2): 89. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in Korean patients with hypercholesterolemia and high cardiovascular risk: subanalysis of the ODYSSEY-KT study
Chang-Wook Nam, Dong-Soo Kim, Jianyong Li, Marie T. Baccara-Dinet, Ivy Li, Ji-Hyun Kim, Chong-Jin Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(6): 1252. CrossRef - Progress of Short-term Herbal Medicine Administration for Hypertriglyceridemia: a Case Report
Bo-min Kim, Hee-geun Jo
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2019; 40(3): 517. CrossRef - Use of fenofibrate on cardiovascular outcomes in statin users with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ki Hoon Han, Jimi Choi, Juneyoung Lee, Sin Gon Kim
BMJ.2019; : l5125. CrossRef - The risk of herpes zoster virus infection in patients with depression
Hyo Geun Choi, Eui-Joong Kim, Young Kyung Lee, Miyoung Kim
Medicine.2019; 98(40): e17430. CrossRef - Effect of Change in Total Cholesterol Levels on Cardiovascular Disease Among Young Adults
Su‐Min Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Kyuwoong Kim, Sung Min Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Seong Yong Park, Yeon‐Yong Kim, Joung Sik Son, Jae‐Moon Yun, Sang Min Park
Journal of the American Heart Association.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin Combination Therapy Versus Those of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy in Patients With Primary Hypercholesterolemia
Woohyeun Kim, Yeonyee E. Yoon, Sung-Hee Shin, Jang-Whan Bae, Bum-Kee Hong, Soon Jun Hong, Ki Chul Sung, Seung Hwan Han, Weon Kim, Moo-Yong Rhee, Sang-Hyun Kim, Sang Eun Lee, Min Su Hyon, Gyo-Seung Hwang, Jang Won Son, Jang-Young Kim, Min Kyu Kim, Sang Woo
Clinical Therapeutics.2018; 40(6): 993. CrossRef - Prevalence of dyslipidemia among the population of a large region of Eastern Siberia and its association with sociodemographic and behavioral factors
Yu. I. Grinshtein, V. V. Shabalin, R. R. Ruf, M. M. Petrova, S. A. Shal'nova
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2018; 21(5): 63. CrossRef
- Association between weekend catch-up sleep and dyslipidemia among Korean workers


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



